In 1905 and 1915, the famous physicist Einstein gave his general and special theories of relativity in which he predicted five objects (namely; Black holes, white holes, wormholes, tippler cylinder and kugel blitz) that must be present in our universe. When he predicted those objects, we did not have ample technology to see one until a whole century later. In 2019, we got the first ever real image of a black hole taken by NASA’s Hubble space telescope.
WHAT IS A BLACK HOLE?
A black hole is a structure comprising very densely packed matter. An event horizon is the boundary of a place where no escape is possible. To understand what a black hole is, we first need to understand some other basic concepts. Every mass (matter) in the entire universe has its gravity proportioned; accordingly, even you have your own but very little gravity. Every force of gravity has some escape velocity. Escape velocity is the minimum speed required to leave that body and is directly proportional to the strength of the force of gravity, which means the higher the mass of the body, the higher its escape velocity. For example, the earth has an escape velocity of about 2000 m/s (meter per second). Light, which is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, has a speed which is the highest speed ever observed by humans (300,000,000 m/s) in the observable universe. A black hole has such an enormous gravity that not even light could escape it even with such a tremendous speed, and with this amount of gravity, it gulps up everything on its way and around it.
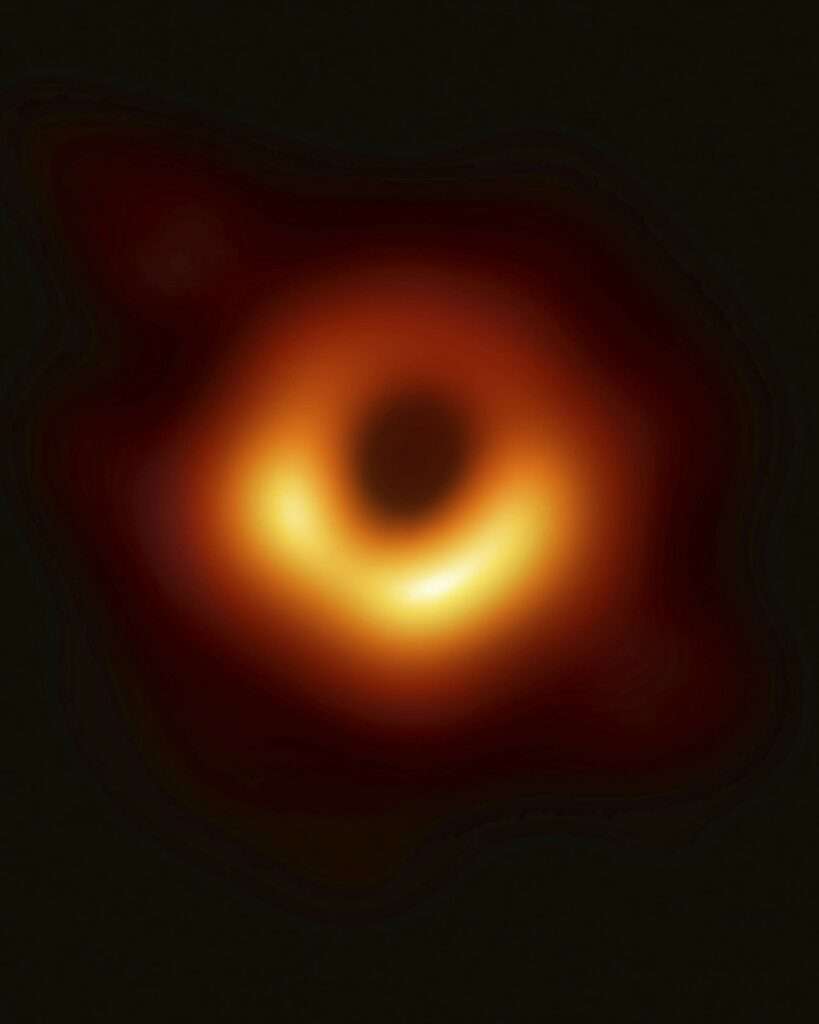
Do you wonder how its image is taken when it does not reflect or absorb light? This picture is not the picture of the black hole itself, but as we know, that black hole gulps up even stars. The luminous sources moving around it produces that light. As gravity tends to attract everything, it also makes it move around for a while, just like stars moving in the disk of a galaxy or moon moving around the earth; the same is the case with a black hole as it tends luminous sources to move around it, but it would be crashing into the black hole far much earlier. These sources allow us to have a picture of the black hole, and if you see that picture, you can see its centre is black, which means no light, while its area along the perimeter is orange due to those luminous sources.
HOW IS A BLACK HOLE FORMED?
As hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, it is almost everywhere. Our space is not a complete vacuum but filled up with three hydrogen atoms per cubic meter. We discussed that all matter has its gravity, and so does hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms attract each other until they form a hydrogen cloud or star-forming region. When it gains enough gravity, this cloud collapses into a spherical body which, under great pressure, starts a fusion reaction and becomes a star more or less like our sun. This star will expand for billions of years and become a red giant, which is about millions or billions of times the sun by mass. It will lose its fuel slowly and form a white dwarf, and at the end, it will explode in a supernova to form a neutron star (a city-sized star but with mass more than the sun) or a black hole. This type of black hole is called a supermassive black hole, but if the star explodes before forming a red giant, it will be a stellar black hole. The main difference between both is size; the supermassive black hole is much bigger.
If two black holes collide together they would produce an enormous gravitational wave. A gravitational wave is a ripple in the fabric of space and time. It is a disturbance in gravitational fields when two gravitational forces come close; they produce a wave that travels at the speed of light. It was first predicted in Einstein’s general theory of relativity, but now we have the technology to detect it in LIGO (laser interferometer gravitational wave observatory) at Hanford Washington and living stone, Louisiana. It is comprised of two 4 KM tunnels placed perpendicular to each other at the ends. A gravitational wave causes the length of the tunnel to stretch or shrink. It is like a trillion mm rod shortened by 5mm. These tunnels have lasers flowing from one end to the other through reflecting mirrors, coming back and detected so that distance is constantly being measured. Through this, we also detected a collision of black holes about 1.3 billion years back and 1.3 billion light-years far from us.
According to Einstein, an object called a kugel blitz could make a black hole. He said that if in a region there is enough concentration of light or energy, it could form a black hole. Some scientists said it could be made if you could generate a sound wave of 1100 decibels, seven times more than the human ear’s capacity to hear. The nearest black hole to earth (V616 MONOCEROTIS) is about 3000 light years away, moving at a speed of 100,000 km/h towards us and is about 9-13 times the sun’s mass.

Saleh ALi
Saleh Ali is an A-level student at Crescent Model School. He is a science enthusiast and loves to read and write about astronomy and cosmology.
Good efforts!!